Vuex@next源码解析 - 工具函数篇篇
前言 🔗
工具函数还是放在一起写,不然感觉有时候写重点的时候,遇到工具函数,要花篇幅去解释会使得文章断层…
工具函数基本在src的utils.js文件下
Vuex工具函数 🔗
find 🔗
export function find(list, f) {
return list.filter(f)[0];
}看他的实现可以看出使用了数组的filter来模拟寻找一个元素
find([1, 2, 3, 4], (val) => val > 2); // 输出3其实感觉可以使用es6的数组方法find的,也能有一样的效果
[1, 2, 3, 4].find((val) => val > 3); // 输出3可能是为了兼容性考虑吧,filter在es5中就已经支持了,而find是es6才有的
forEachValue 🔗
export function forEachValue(obj, fn) {
Object.keys(obj).forEach((key) => fn(obj[key], key));
}对对象进行遍历,传入的回调第一个参数为属性值,第二个参数为属性名
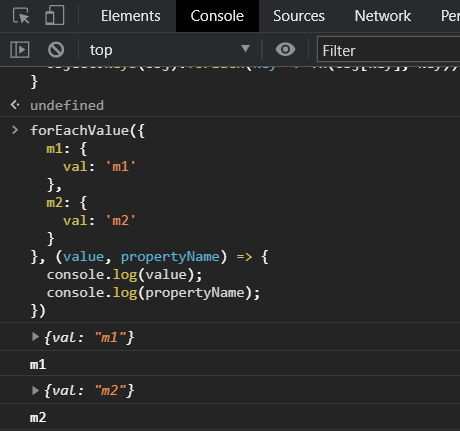
forEachValue(
{
m1: {
val: "m1",
},
m2: {
val: "m2",
},
},
(value, propertyName) => {
console.log(value);
console.log(propertyName);
},
);效果图
这个函数在Vuex的主要代码中使用比较多
isObject 🔗
export function isObject(obj) {
return obj !== null && typeof obj === "object";
}判断是否为对象,注意js中typeof null === 'object',所以null的情况要排除
isPromise 🔗
function isPromise(val) {
return val && typeof val.then === "function";
}Promise/A+规范并没规定如何生成一个Promise
规范只定义了then函数的行为,这里满足存在then函数,即可认为它是一个Promise
这算是一种比较宽松的判断吧
assert 🔗
export function assert(condition, msg) {
if (!condition) throw new Error(`[vuex] ${msg}`);
}这个函数是Vuex用来断言的一个工具函数,通过condition参数为false就抛出错误,统一以[vuex]为前缀字符串
partial 🔗
export function partial(fn, arg) {
return function () {
return fn(arg);
};
}这个函数从名字看挺迷惑的,partial意思:部分的,不完全的
emmm,好吧,单纯从名字看无法推出函数内容
但是从实现看就非常清楚了,这不就是绑定函数的参数然后延迟这个函数的执行吗
deepCopy 🔗
export function deepCopy(obj, cache = []) {
// just return if obj is immutable value
if (obj === null || typeof obj !== "object") {
return obj;
}
// if obj is hit, it is in circular structure
const hit = find(cache, (c) => c.original === obj);
if (hit) {
return hit.copy;
}
const copy = Array.isArray(obj) ? [] : {};
// put the copy into cache at first
// because we want to refer it in recursive deepCopy
cache.push({
original: obj,
copy,
});
Object.keys(obj).forEach((key) => {
copy[key] = deepCopy(obj[key], cache);
});
return copy;
}这个函数应该是这个工具函数中最有意思的了吧,这个函数根据名字上看就是深拷贝的意思、
函数有注释,如下
Deep copy the given object considering circular structure. This function caches all nested objects and its copies. If it detects circular structure, use cached copy to avoid infinite loop.
大概意思是,深拷贝传入的对象,并且考虑到循环引用的情况 这个函数缓存了所有嵌套的对象和他的拷贝 如果发现存在循环引用,使用缓存的拷贝来避免无限的循环
// just return if obj is immutable value
if (obj === null || typeof obj !== "object") {
return obj;
}第一个判断好理解,如果传入的不是一个对象,那么直接返回即可,这里包括了null
deepCopy(1); // 返回1
deepCopy("Hello World!"); // 返回'Hello World'
deepCopy(true); // 返回true
deepCopy(null); // 返回null
deepCopy(undefined); // 返回undefined
deepCopy(function () {}); // 返回function() {} 和入参是同一个函数// if obj is hit, it is in circular structure
const hit = find(cache, (c) => c.original === obj);
if (hit) {
return hit.copy;
}第二部分会在cache数组中查找是否已经登记过这个对象了
如果登记过了,那么此时就是不应该拷贝这个对象了,直接返回它前面登记的拷贝对象
const copy = Array.isArray(obj) ? [] : {};
// put the copy into cache at first
// because we want to refer it in recursive deepCopy
cache.push({
original: obj,
copy,
});这一段就是把拷贝的对象和原对象登记到cache数组里面
这里可以看出这个深拷贝只支持字面对象和数组,不支持Set或者Map等
不过我感觉这也涵盖了许多的情况了,通用性感觉还是挺高的
Object.keys(obj).forEach((key) => {
copy[key] = deepCopy(obj[key], cache);
});
return copy;接着就是通过Object.keys来递归的深拷贝每个属性对应的值,然后返回当前的拷贝出来的对象
整体上我们可以测试下
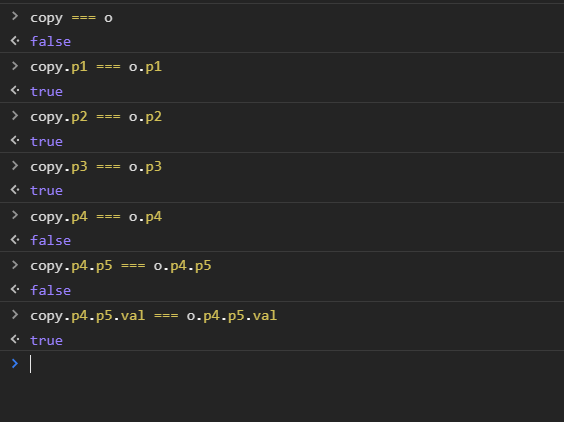
const o = {
p1: 1,
p2: "2",
p3: function () {
console.log("3");
},
p4: {
p5: {
val: 1,
},
},
};
const copy = deepCopy(o);
copy === o; // false
copy.p1 === o.p1; // true
copy.p2 === o.p2; // true
copy.p3 === o.p3; // true
copy.p4 === o.p4; // false
copy.p4.p5 === o.p4.p5; // false
copy.p4.p5.val === o.p4.p5.val; // true测试如下
后记 🔗
目前Vuex的源码解析的文章还在改进中,如果你幸运地来到了这里,也对我的帖子感兴趣,
那么请再给我一点时间,让我更好地整理和调整文章的细节,谢谢😘