Spring中Bean的配置方式
发表于2020-06-11
更新于2023-02-13
总字数1.1K
阅读时长 ≈4 分钟
前言 🔗
困了就数珈百璃
数到33就可以睡着
####准备
一个spring的Java项目
这个之前有写
有需要的可以自己翻阅
XML配置 🔗
有两种配置吧~~(我知道的)~~
- 构造器的注入方式
- setter注入方式
先建两个类
User(用户)类和Role(角色)类
java
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private List<Role> list;
// 省略getter和setter方法
}java
public class Role {
private int id;
private String name;
// 省略getter和setter方法
}下面都会用这两个类作例子
setter注入方式 🔗
这里用Role类作例子
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--id:配置这个bean的唯一标识,Spring通过id获取这个bean-->
<!--class:指定是哪个类,用于反射,注入值-->
<bean id="role" class="pojo.Role">
<!--property的name属性对应类的属性名-->
<!--可以直接再property中内嵌value属性指定值-->
<!--也可以通过value子标签指定值,如下所示-->
<property name="id">
<value>1</value>
</property>
<property name="name" value="管理员"></property>
</bean>
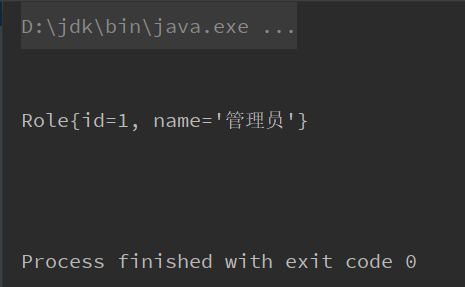
</beans>写个测试类测试下执行test01测试方法
java
public class SpringBeanTest {
@Test
public void test01() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
Role role = applicationContext.getBean("role", Role.class);
System.out.println(role);
applicationContext.close();
}
}发现可以成功地注入属性
使用setter注入要注意
需要注入的属性必须有对应的setter方法
才能注入成功,不然会报错
构造器(constructor)注入方式 🔗
这里用User类作例子
构造器注入的话
必须有对应参数的构造函数
也就是User类必须做一点修改
java
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private List<Role> list;
public User() {}
// 添加一个有参构造
public User(int id, String name, List<Role> list) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.list = list;
}
// 省略getter和setter方法
}xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="role" class="pojo.Role">
<property name="id">
<value>1</value>
</property>
<property name="name" value="管理员"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="user" class="pojo.User">
<!--constructor-arg表示一个构造器参数-->
<!--和property一样可以内嵌value指定值,也可以写子value标签指定值-->
<constructor-arg value="1"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg>
<value>lwf</value>
</constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg>
<!--配置一个List集合-->
<list>
<!--引用id为role的bean作为集合的值-->
<ref bean="role"></ref>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
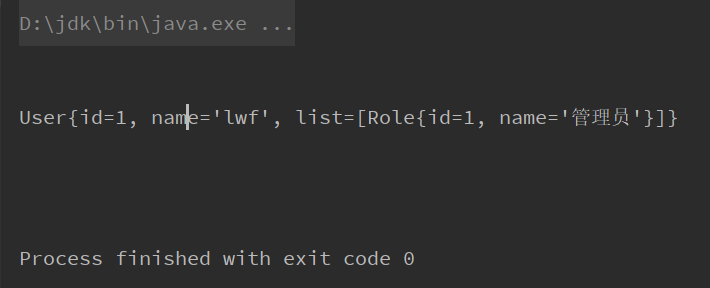
</beans>测试一下,运行test02
java
public class SpringBeanTest {
@Test
public void test02() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
User user = applicationContext.getBean("user", User.class);
System.out.println(user);
applicationContext.close();
}
}发现可以成功注入
使用构造器注入要注意
构造器参数的顺序必须和构造函数的传入参数的顺序一样
不然会报错
setter注入和构造器注入可以混合使用
但是构造器注入参数的顺序必须和构造函数的参数顺序保持一致
注解 🔗
使用注解方式也需要xml的文件
不过xml文件只需要简单的配置
表明开启注解方式来配置Bean
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--开启注解配置-->
<!--表明扫描pojo包下的类-->
<context:component-scan base-package="pojo"/>
</beans>然后就是通过注解方式来配置
这里用Role作例子
java
// 这里的value指定bean的唯一id,也就是对应bean标签中的id属性
// 如果不指定的话,就会默认使用类名的小写表示
// 即 Role -> role
@Component(value = "role")
public class Role {
// 通过Value注解注入值
@Value("1")
private int id;
@Value("管理员")
private String name;
// 省略getter和setter方法
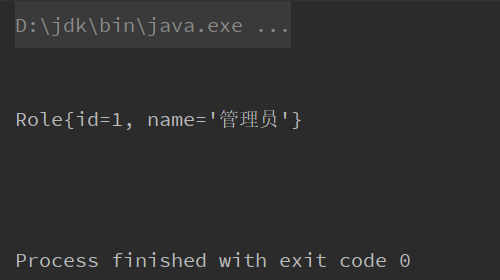
}测试一下
java
public class SpringBeanTest {
@Test
public void test03() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
Role role = applicationContext.getBean("role", Role.class);
System.out.println(role);
applicationContext.close();
}
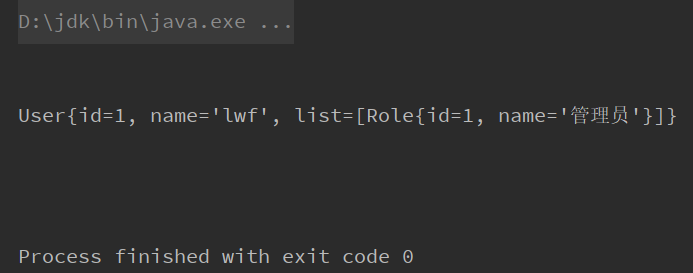
}发现可以成功注入
再用User作例子
java
@Component(value = "user")
public class User {
@Value("1")
private int id;
@Value("lwf")
private String name;
// Autowired自动注入
// 对于集合来说,spring会把所有类型为Role的对象注入集合中
// 对于map来说,spring会把id作为key,对象作为value注入map中
// 对于一个对象,默认根据类型进行匹配,如果匹配不到,就会去找名字(id)
@Autowired
private List<Role> list;
// 省略getter和setter方法
}测试下
java
public class SpringBeanTest {
@Test
public void test04() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
User user = applicationContext.getBean("user", User.class);
System.out.println(user);
applicationContext.close();
}
}哦呐该,如果没有评论的话,瓦达西...