Typescript中的工具类型
前言 🔗
写写那些Typescript自带的工具类型吧,可能原理方面偏少,更多的是翻译
正文 🔗
Typescript自带的工具类型,有些在源码中也经常的使用到,比如Record在Vue@next中就有用到
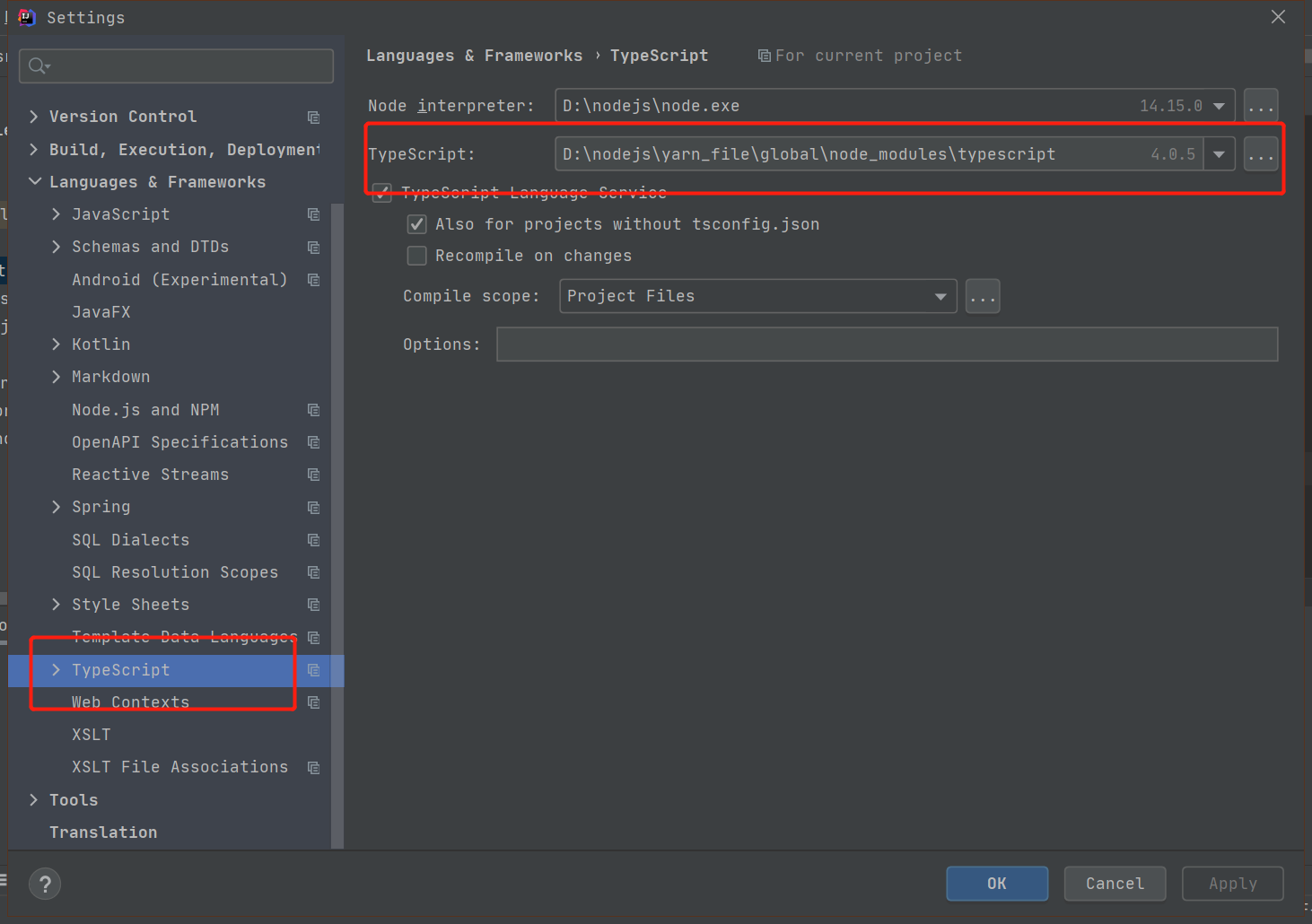
为了在IDE中使用Typescript,本文使用全局安装方式(yarn global add typescript,npm为npm install -g typescript)
然后在IDEA的Typescript配置安装路径
IDEA 2020.2默认有内置的Typescript,版本为3.9.5,不过现在是4.0.5了
Partial<T> 🔗
Constructs a type with all properties of 'T' set to optional.
This utility will return a type that represents all subsets of a given type.
构造一个传入类型T的所有属性都为可选的类型
简单地讲就是使得泛型T的所有属性变为可选的
interface User {
id: number;
name: string;
}
// id和name都变成可选的了
type UserPartial = Partial<User>;
function fn(userPartial: UserPartial) {}
fn({}); // 可以
fn({ id: 1 }); // 可以
fn({ name: "lwf" }); // 可以可以看下它的源码
/**
* Make all properties in T optional
*/
type Partial<T> = {
[P in keyof T]?: T[P];
};使用keyof来获取全部的属性名,然后使用in来遍历,使用?使得属性变为可配置,右侧的值为T[P]对应每个属性对应的类型
Readonly<T> 🔗
Constructs a type with all properties of 'T' set to readonly,
meaning the properties of the constructed type cannot be reassigned.
构造一个传入类型T的所有属性都为只读的类型,这意味着构造出来的类型的属性无法被重新赋值
interface User {
id: number;
name: string;
}
type UserReadOnly = Readonly<User>
const user: UserReadOnly = {
id: 1,
name: "lwf"
};
user.id = 1; // 报错
user.name = "fwl" // 报错注意这里的只读只对这个对象的属性生效,嵌套的属性不生效
interface User {
id: number;
name: string;
info: {
age: number;
sex: "male" | "female";
}
}
type UserReadOnly = Readonly<User>
const user: UserReadOnly = {
id: 1,
name: "lwf",
info: {
age: 22,
sex: "male"
}
};
user.info = {
age: 11,
sex: "female"
}; // 报错
user.info.age = 11; // 可以源码如下
/**
* Make all properties in T readonly
*/
type Readonly<T> = {
readonly [P in keyof T]: T[P];
};依然使用keyof来获取全部的属性名,然后使用in来遍历,右侧值为对应的类型
然后对每个属性前都用readonly来标注,使之成为只读的
如果想让一个数组变为只读,可以使用Readonly<Array<T>>,比如
const arr: Readonly<Array<any>> = [];
arr[1] = 1; // 报错其实Typescript已经内置了只读的数组类型ReadonlyArray<T>
const arr: ReadonlyArray<number> = [];
arr[1] = 1; // 报错对于ReadonlyArray和Array的区别就是
ReadonlyArray在整数属性和length上使用了readonly来修饰,而Array没有
并且ReadonlyArray少了那些会使得数组发送改变的方法,比如push,pop,shift,unshift,如下(省略了注释以及相同的API)
interface Array<T> {
length: number;
pop(): T | undefined;
push(...items: T[]): number;
reverse(): T[];
shift(): T | undefined;
sort(compareFn?: (a: T, b: T) => number): this;
splice(start: number, deleteCount?: number): T[];
splice(start: number, deleteCount: number, ...items: T[]): T[];
unshift(...items: T[]): number;
[n: number]: T;
// 其他API...
}
interface ReadonlyArray<T> {
readonly length: number;
readonly [n: number]: T;
// 其他API...
}sort和reverse由于会交换数组中元素的位置(交换步骤会涉及到赋值),所以没有在ReadonlyArray中
Record<K, T> 🔗
Constructs a type with a set of properties 'K' of type 'T'.
This utility can be used to map the properties of a type to another type.
构造一个属性为K的集合,属性对应的类型为T的类型 这个工具类型可以把一个类型的属性映射到另一个类型
let record: Record<string, Function>;
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
record[i] = function () {
return i + 1;
}; // 可以
}
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
record[i] = i + 1; // 报错
}源码如下
type Record<K extends keyof any, T> = {
[P in K]: T;
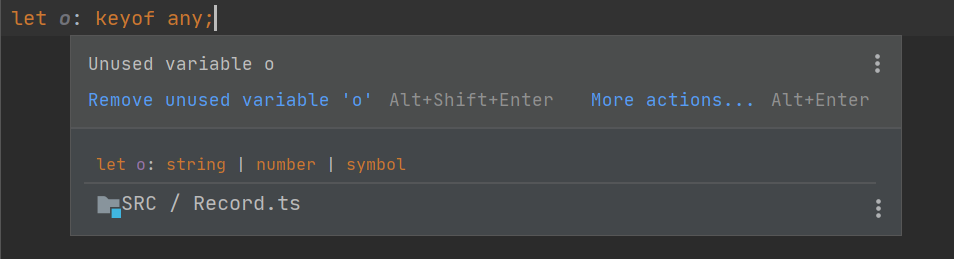
};这里可能会疑惑keyof any是个什么东西,可以试着给某个变量赋予看一下
发现变量o类型为number或者symbol或者number
也就是泛型K必须是这三个类型中的其中一种,如果使用Function作为范型K,是无效的
let record: Record<Function, string>; // 报错一般都是使用Record<string, T>来生成一个类型为T的映射对象
Pick<T, K> 🔗
Constructs a type by picking the set of properties 'K' from 'T'.
构造一个从T中选取K属性集的类型
interface User {
id: number;
name: string;
}
// 现在UserPick类型只有id属性了
type UserPick = Pick<User, "id">;
let user: UserPick = {
id: 1
}; // 可以
user.name = "lwf"; // 报错源码如下
type Pick<T, K extends keyof T> = {
[P in K]: T[P];
};keyof T获取T的属性集,依然使用in来遍历属性集,每个属性对应类型为T[P]
这里可以看出K必须是T属性集的一个子集,不是的话会报错
interface User {
id: number;
name: string;
}
// age没有在User中,报错
type UserPick = Pick<User, "id" | "age">;Omit<T, K> 🔗
Constructs a type by picking all properties from 'T' and then removing 'K'.
构造一个从T中移除K属性集的类型
interface User {
id: number;
name: string;
}
// id被移除了,现在只有name了
type UserOmit = Omit<User, "id">;
let user: UserOmit = {
name: "lwf"
}; // 可以
user.id = 1; // 报错源码如下
type Omit<T, K extends keyof any> = Pick<T, Exclude<keyof T, K>>;可以看到,实现依赖了Pick和Exclude,可以先在左边点击Exclude查看
Exclude<keyof T, K>提取T中不包含K的部分,这时得到的只是属性名的集合类型,而不是属性名对应属性值类型
再使用Pick<T, Exclude<keyof T, K>>把这部分提取出来,这时就变成属性名对应属性值类型
Exclude<T, E> 🔗
Constructs a type by excluding from 'T' all union members that are assignable to 'E'.
构造一个从T中排除所有可以分配给E的联合成员的类型
type t1 = Exclude<"a" | "b" | "c", "c">; // "a" | "b"
type t2 = Exclude<string | number, 1 | "" | false>; // string | number
type t3 = Exclude<1 | "" | false, string | number>; // false类型t1应该很好理解,有趣的应该是t2和t3
t2由于number无法分给1,以及string无法分给空字符串,所以还是string | number
而t3和t2相反,1可以分给number,以及空字符串可以分给string,所以t3类型为false
Extract<T, U> 🔗
Constructs a type by extracting from 'T' all union members that are assignable to 'U'.
构造一个从T中提取所有可以分配给E的联合成员的类型
这个和Exclude<T, E>相反,大白话就是求交集,但是有单向的关系
type t1 = Extract<"a" | "b" | "c", "c">; // "c"
type t2 = Extract<string | number, 1 | "" | false>; // never
type t3 = Extract<1 | "" | false, string | number>; // 1 | ""t1还是很好理解,重点还是t2和t3
t2由于string无法分给空字符串,以及number无法分给1,导致"并集"为空,所以为never
t3由于1可以分给number,以及空字符串可以分给string,所以并集就为1 | ""
源码如下
type Extract<T, U> = T extends U ? T : never; NonNullable<T> 🔗
Constructs a type by excluding null and undefined from 'T'.
构造一个从T中排除null和undefined的类型
type t = NonNullable<number | string | null | undefined>; // number | string源码如下
type NonNullable<T> = T extends null | undefined ? never : T;Parameters<T> 🔗
Constructs a tuple type from the types used in the parameters of a function type 'T'.
构造一个类型T函数的参数类型的元素类型
通俗点讲就是提取函数的参数,用数组装起来
type f1 = (id: number, name: string) => void;
type args = Parameters<f1>; // [ id: number, name: string ]源码如下
type Parameters<T extends (...args: any) => any> = T extends (...args: infer P) => any ? P : never;ConstructorParameters<T> 🔗
Constructs a tuple or array type from the types of a constructor function type.
It produces a tuple type with all the parameter types (or the type never if Type is not a function).
构造一个从构造函数的类型的元组或者数组类型,产生了一个所有参数类型的元组类型(或者当T不是一个函数时为never类型)
简单点讲就是提取构造函数的参数类型
interface User {
new(id: number, name: string): void
}
type UserParameters = ConstructorParameters<User>; // [ id: number, name: string ]源码如下
type ConstructorParameters<T extends new (...args: any) => any> = T extends new (...args: infer P) => any ? P : never;这里和Parameters的区别就是ConstructorParameters必须为构造函数,而Parameters必须为普通函数,两着无法相互转换
ReturnType<T> 🔗
Constructs a type consisting of the return type of function 'T'.
构造一个由T函数类型的返回类型组成的类型
简单点讲就是提取函数返回的类型
interface User {
id: number;
name: string;
}
interface UserService {
getUser(id: User["id"]): User;
}
type getUserReturnType = ReturnType<UserService["getUser"]>; // User源码如下
type ReturnType<T extends (...args: any) => any> = T extends (...args: any) => infer R ? R : any;InstanceType<T> 🔗
Constructs a type consisting of the instance type of a constructor function in 'T'.
构造一个T构造函数的实例类型的类型
简单点讲就是返回某个构造函数产生的实例的类型
interface User {
new(id: number, name: string): string;
}
type a = InstanceType<User> // string源码如下
type InstanceType<T extends new (...args: any) => any> = T extends new (...args: any) => infer R ? R : any;Required<T> 🔗
Constructs a type consisting of all properties of 'T' set to required.
The opposite ofPartial.
构造一个T类型的所有属性集都是必须的类型 是Partial操作的相反操作
interface User {
id: number;
name?: string;
}
type UserRequired = Required<User>;
let user: UserRequired = {
id: 1
}; // 报错,提示缺失name源码如下
type Required<T> = {
[P in keyof T]-?: T[P];
};ThisParameterType<T> 🔗
Extracts the type of the this parameter for a function type,
or unknown if the function type has no this parameter.
提取一个函数类型的this参数类型, 如果函数类型没有this参数,那么为unknown
type Context = {
id: number;
name: string;
}
type f1 = (this: Context) => void;
type t = ThisParameterType<f1>; // Context源码如下
type ThisParameterType<T> = T extends (this: infer U, ...args: any[]) => any ? U : unknown;OmitThisParameter<T> 🔗
Removes the this parameter from
T. IfThas no explicitly declared this parameter, the result is simplyT.
Otherwise, a new function type with no this parameter is created fromT.
Generics are erased and only the last overload signature is propagated into the new function type.
删除T的this参数,如果T没有明确的定义this参数,结果为简单的T 否则,从T生成一个没有this参数的新的函数类型 泛型会被擦除,只有最后的重载签名会被传递到新的函数类型中。
type Context = {
id: number;
name: string;
}
type f1 = (this: Context, age: number) => void;
type t = OmitThisParameter<f1>; // (age: number) => void源码如下
type OmitThisParameter<T> = unknown extends ThisParameterType<T> ? T : T extends (...args: infer A) => infer R ? (...args: A) => R : T;ThisType<T> 🔗
This utility does not return a transformed type. Instead, it serves as a marker for a contextual this type.
Note that the --noImplicitThis flag must be enabled to use this utility.
这个工具不会返回一个转换的类型,而是用于标记一个this的上下文的类型 使用--noImplicitThis标志才能够使用这个工具
这个有点混入的意思在里面,这里借用官方的例子,记得在tsconfig.json中配置
{
"compilerOptions": {
"noImplicitThis": true
}
}例子
type ObjectDescriptor<D, M> = {
data?: D;
methods?: M & ThisType<D & M>; // Type of 'this' in methods is D & M
};
function makeObject<D, M>(desc: ObjectDescriptor<D, M>): D & M {
let data: object = desc.data || {};
let methods: object = desc.methods || {};
return { ...data, ...methods } as D & M;
}
let obj = makeObject({
data: { x: 0, y: 0 },
methods: {
moveBy(dx: number, dy: number) {
this.x += dx;
this.y += dy;
// 如果没有加ThisType<D & M>,这里点不到x和y
},
},
});源码如下
interface ThisType<T> { }后记 🔗
重装了下npm和yarn,明明把安装路径放D盘了,还是装到C盘…
看起来还是非常不错的工具类,不过实现还是有些看不懂,比如泛型的?:加上extends,得找个时间好好看看…
以及一些有趣的语法,比如infer,readonly,-?等